This post is the latest in an ongoing series about how we harness the data we collect to improve our products and services for our users. - Ed. What if you could do a little something to improve the world during your daily drive to work? Here are a few ideas: tell everybody in the city when you're stuck in slow-moving traffic; warn the drivers on the freeway behind you that they should consider an alternate route; tell the people still at home that they should spend another ten minutes reading the morning news before they leave for work; tell your city government that they might want to change the timing of that traffic light at the highway on-ramp. Of course, you can't just get on the phone and call everybody, and your one traffic report from your one spot on the road might not help much anyway. But if everybody on the road, all at once, could tell the world how fast their car is moving, and we could make it easy for anybody to check that information on their computer or cell phone, well — then we'd be getting somewhere.
If you use
Google Maps for mobile with GPS enabled on your phone, that's exactly what you can do. When you choose to enable Google Maps with
My Location, your phone sends anonymous bits of data back to Google describing how fast you're moving. When we combine your speed with the speed of other phones on the road, across thousands of phones moving around a city at any given time, we can get a pretty good picture of live traffic conditions. We continuously combine this data and send it back to you for free in the Google Maps traffic layers. It takes almost zero effort on your part — just turn on Google Maps for mobile before starting your car — and the more people that participate, the better the resulting traffic reports get for everybody.
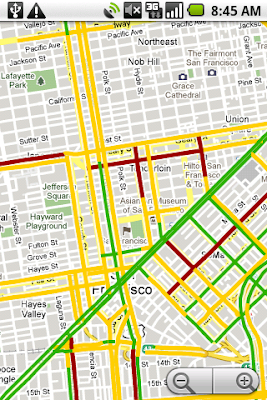
This week we're
expanding our traffic layer to cover all U.S. highways and arterials when data is available. We're able to do this thanks in no small part to the data contributed by our users. This is exactly the kind of technology that we love at Google because it's so easy for a single person to help out, but can be incredibly powerful when a lot of people use it together. Imagine if you knew the exact traffic speed on every road in the city — every intersection, backstreet and freeway on-ramp — and how that would affect the way you drive, help the environment and impact the way our government makes road planning decisions. This idea, which we geeks call "crowdsourcing," isn't new. Ever since GPS location started coming to mainstream devices, people have been thinking of ways to use it to figure out how fast the traffic is moving. But for us to really make it work, we had to solve problems of scale (because you can't get useful traffic results until you have a LOT of devices reporting their speeds) and privacy (because we don't want anybody to be able to analyze Google's traffic data to see the movement of a particular phone, even when that phone is completely anonymous).
We achieve scale by making Google Maps for mobile easy to install and use, and by making it easy for people to provide information about their own vehicle speed. There's no extra device to plug into your car and no extra software to buy. Google Maps is
free and works with most cell phones, and the number of cell phones with GPS is rising every day. Some phones, such as the T-Mobile myTouch 3G and the Palm Pre, come with Google Maps and traffic crowdsourcing pre-installed (the iPhone Maps application, however, does not support traffic crowdsourcing). Google is fortunate to have a lot of people using our products, and that scale helps make our products better.
We understand that many people would be concerned about telling the world how fast their car was moving if they also had to tell the world where they were going, so we built privacy protections in from the start. We only use anonymous speed and location information to calculate traffic conditions, and only do so when you have chosen to enable location services on your phone. We use our scale to provide further privacy protection: When a lot of people are reporting data from the same area, we combine their data together to make it hard to tell one phone from another. Even though the vehicle carrying a phone is anonymous, we don't want anybody to be able to find out where that anonymous vehicle came from or where it went — so we find the start and end points of every trip and permanently delete that data so that even Google ceases to have access to it. We take the privacy concerns related to user location data seriously, and have worked hard to protect the privacy of users who share this data — but we still understand that not everybody will want to participate. If you'd like to stop your phone from sending anonymous location data back to Google, you can find opt-out instructions
here.
We've already been able to provide useful traffic information with the help of our existing mobile users, but we hope that is just the start. As GPS-enabled phones and data plans get less expensive, more people will be able to participate. Crowdsourcing traffic gives us a way to harness bits of location data from our users and give it back to them in a form they can use to make impactful decisions that affect their free time, their pocketbooks and the environment. The more people use it, the better it will get. So next time you're sitting in morning traffic, turn on Google Maps for mobile and let someone else know they can hit the snooze button one more time. Tomorrow morning, they might do the same for you.
Posted by Dave Barth, Product Manager for Google Maps

















































